Introduction:- Power in the Sky: The Rise of Drone-to-Drone Charging:
Drone-to-drone charging is an emerging trend in the advancement of drone technology, as the number of drone features (improved functionality, faster speed, and increased capabilities) continues to increase. Drones have many uses, including delivery of goods, photography from above, support for farmers, security/safety surveillance, and support for emergency response. However, battery capacity prevents the vast majority of drone applications from realizing their full potential. Many drones currently being commercially manufactured only fly for a short amount of time and need to land regularly to recharge their batteries.
To address this situation, many creative engineers are developing new ways to recharge drones (or drone-to-drone charging systems). Drone-to-drone charging systems allow a drone to recharge another drone while both drones are flying in the air.
This article will outline and describe how drone-to-drone charging systems work and their potential uses and benefits in current and future drone applications. This article will discuss the challenges associated with drone-to-drone charging systems and highlight the importance of this technology to all future uses of drone technology.1. What Is Drone-to-Drone Charging?
Charging a drone with another drone is when one drone provides power to another while they are both in flight. The working drone continues to fly and is recharged in mid-air instead of having to land at a charging station or base. This concept was derived from a military aircraft’s capability to refuel in mid-air through aerial refueling but has been modified to work with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) using automated technology and advanced controls.
a. Extended Flight Time
Drone-to-drone charging allows UAVs to stay airborne longer by recharging mid-air without landing.
b. Reduced Dependence on Ground Stations
This system minimizes the need for fixed charging stations, making drone operations possible in remote or difficult environments.
c. Intelligent Mid-Air Docking and Control
Advanced sensors, cameras, and AI help drones safely align, connect, and maintain stability during the charging process.
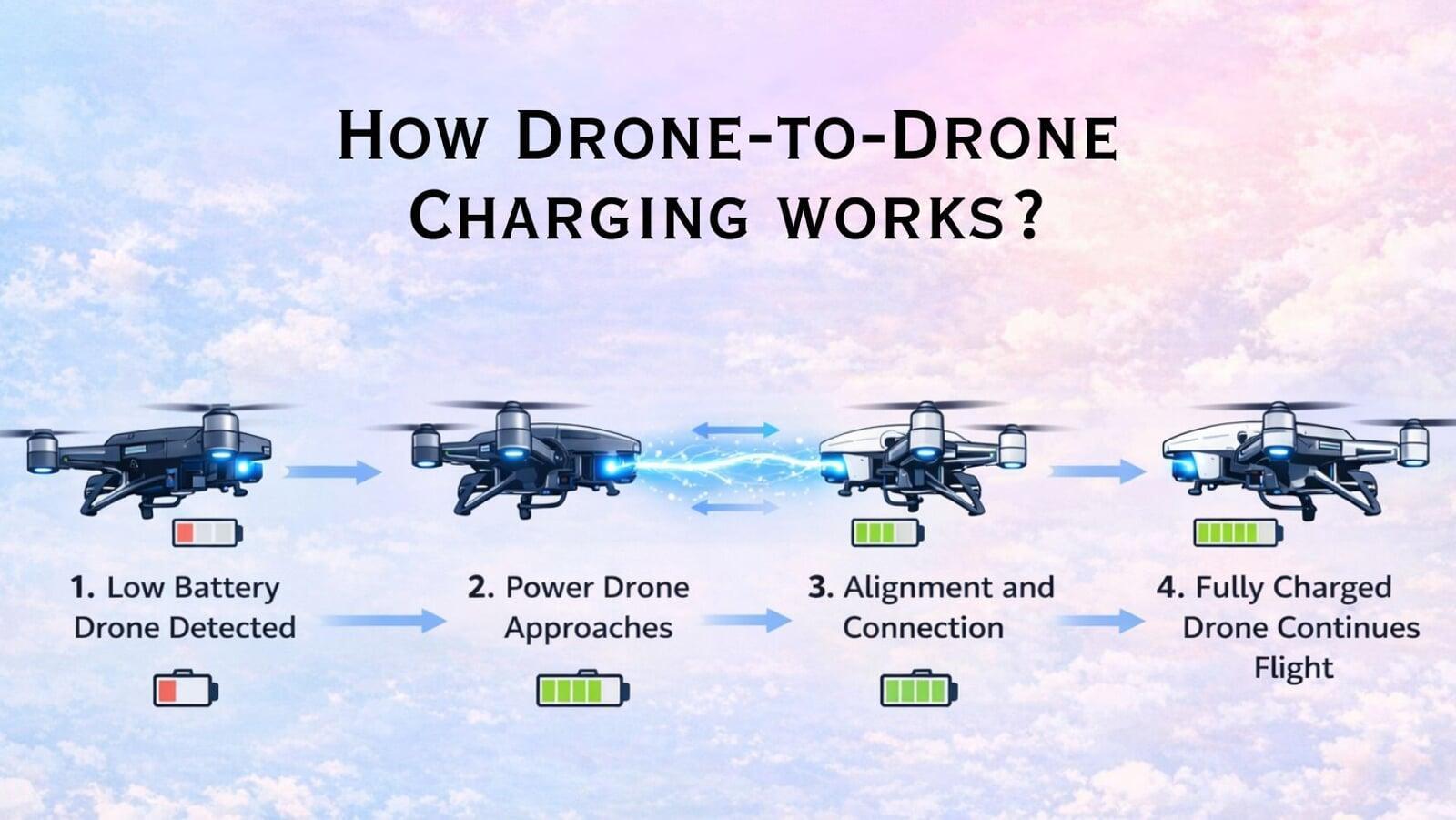
2. How Drone-to-Drone Charging Works?
a. The technology continues to develop, but the basic operation is quite straight forward.
b. Low battery voltage detected by a mission drone
c. Base station issues a charging drone
d. Charging drone meets mission drone at predetermined altitude
e. Power is transferred by means of a charging system
f. The mission drone continues its mission
g. Charging drone supports the mission drone and/or returns to base station
h. The entire system has been developed to be as safe, automatic and efficient as possible. The entire process is designed to be automated, safe, and efficient.
3. Types of Drone-to-Drone Charging Methods
a. Wired Mid-Air Charging:-
Two drones are physically connected with wire for a short time. The connection allows for a faster charge, but it requires a high level of accurate alignment and stability.
b. Wireless Charging:-
- Wireless charging uses an electromagnetic field or resonant charging technologies.
- Wireless charging utilises electromagnetic fields to transmit empiric power between two devices.
- Wireless charging technologies have been considered to be very safe but are slower than wired charging, as the technology is still in early stages of development.
c. Docking-Based Charging:-
The receiver drone is presented to the charging drone like a flying station. Docking based charges provide better control and energy transfer efficiency.
d. Importance of Drone-to-Drone Charging:-
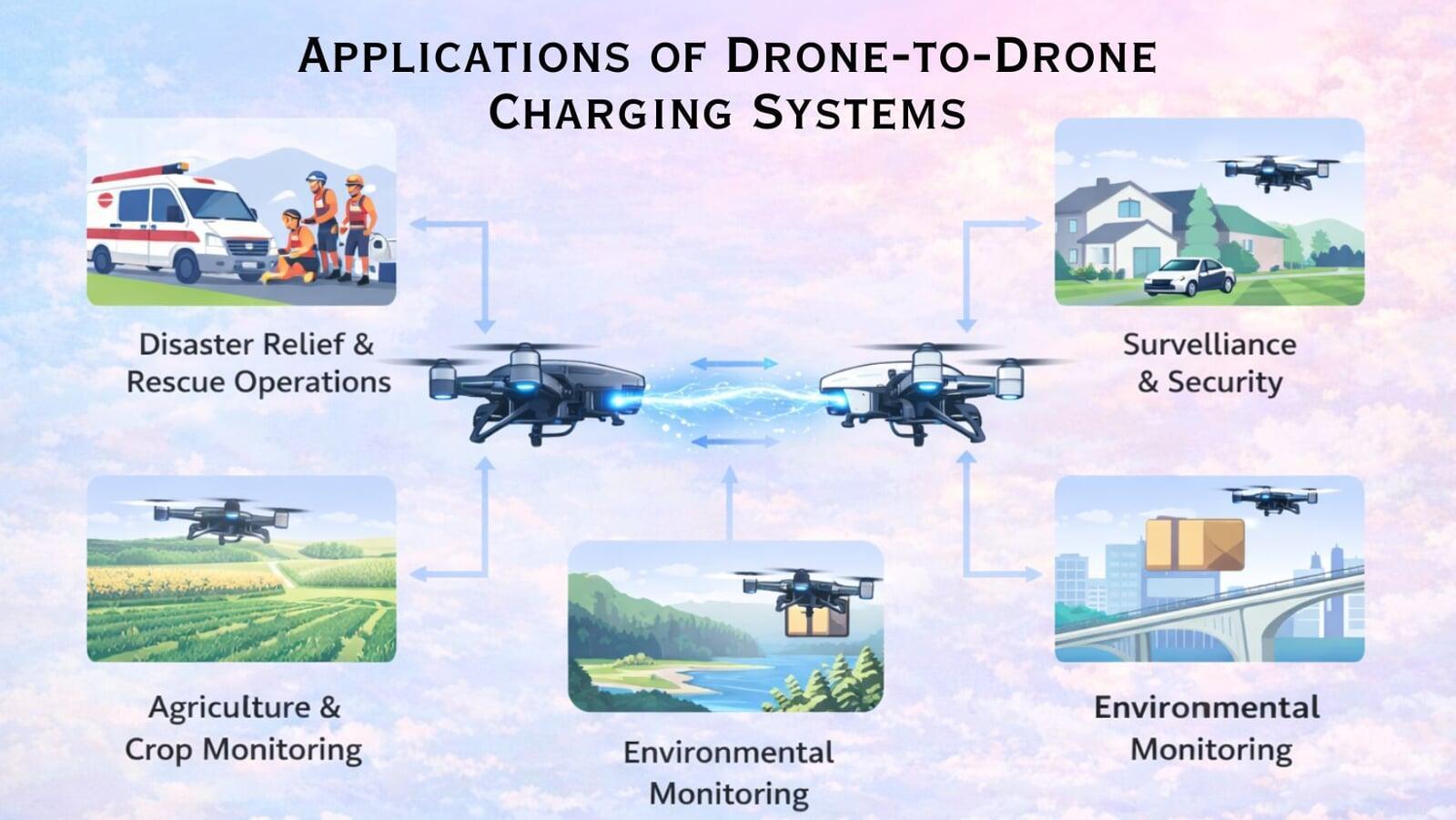
The limitations of batteries restrict the range and endurance of drone operations. The use of Drone to Drone charging extends the flight times of the drones, reduces downtime, and eliminates the need for frequent landings, increasing the overall efficiency of drone operations. With this technology, drones can now stay in the air for period of hours rather than just minutes.4. Applications of Drone-to-Drone Charging Systems:
a. Logistics and Delivery
Drones are able to recharge each other in flight, allowing logistics operations and delivery vehicles (drones) to conduct long-haul flights without returning to warehouses for recharging.
b. Defense and Surveillance
There is no need to land military surveillance (drones) in order to safely recharge them so they can remain in the air for longer periods.
c. Disaster Management
In the event of a disaster (i.e., flood or earthquake) drones will be able to provide uninterrupted operational support for a variety of rescue, mapping and supply delivery applications.
d. AgricultureUsing an agricultural drone will allow you to fly over larger agricultural production areas without requiring the need for multiple recharging.
e. Communication and Monitoring
Drones that can serve as a temporary communications tower can be kept operational longer.5. Advantages of Drone-to-Drone Charging:
Drone-to-drone charging has a variety of advantages. In particular, the ability to charge drones while they are in the air greatly increases the ability of drones to perform future missions.
a. Increased Operating Efficiency and Greater Time Efficiency –
By enabling ongoing drone operations (which eliminates downtime during recharging) the amount of data collected and tasks accomplished on each flight will be maximized.
b. Reduced Requirement for Ground-Based Charging Stations –
The reduced number of recharging stations required to maintain and support drone operations will result in decreased capital expenditures and greater operational flexibility for the operators.
c. Reduced Delays in Mission Completion Due to Battery Swaps –
This will lead to faster mission completion times because there will no longer be a need to stop a mission in the middle of it to swap batteries.
d. Ideal Solution For Remote Locations
Conclusion: This is an ideal solution for areas where there may not be recharging capabilities or landing areas.6. The main Challenges of Charging Technology:
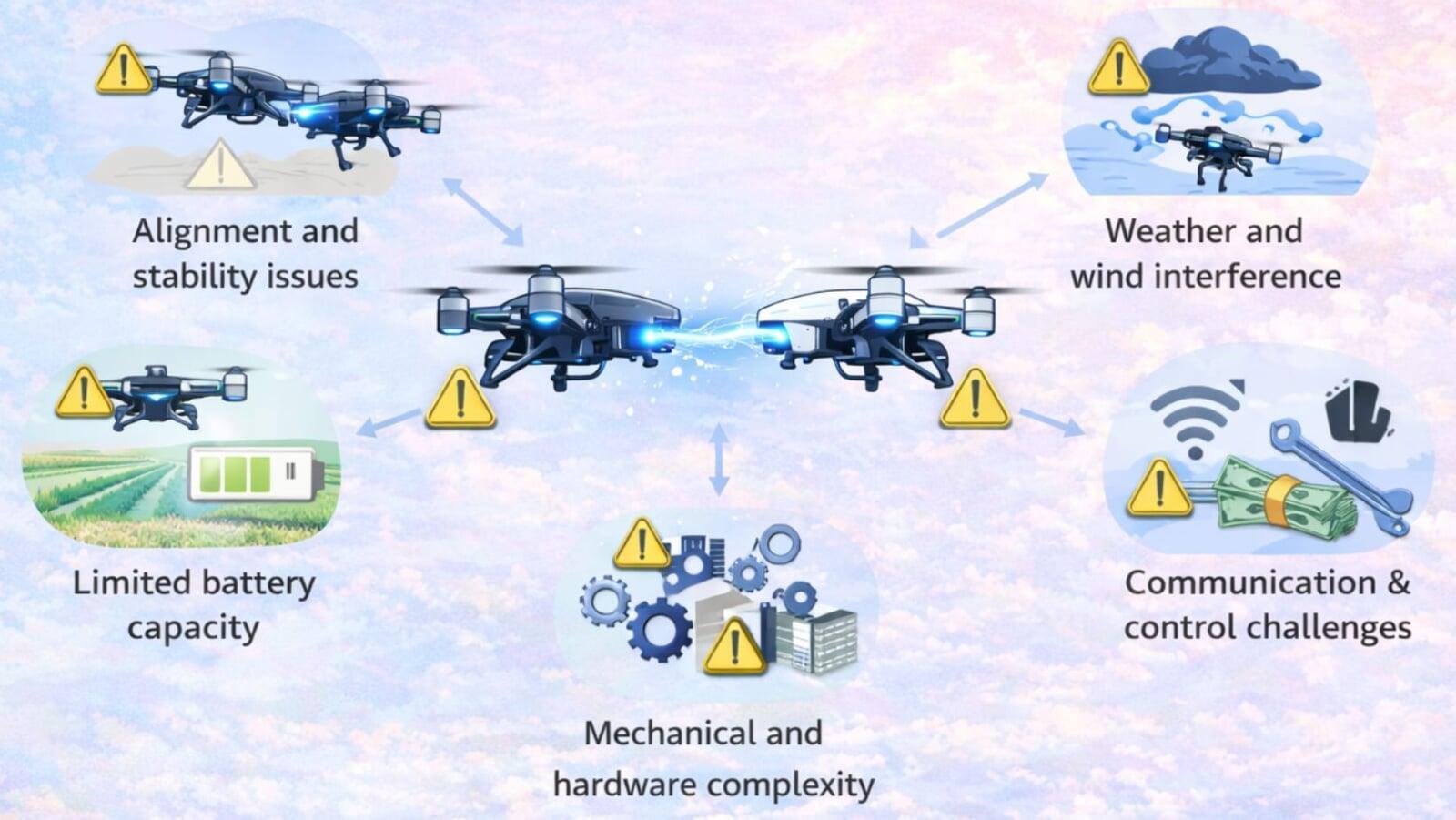
a. Charging Technology Has a Very High Level of Technical Complexity -
Mid-Air Charging is a technology that requires the ability for carriers to navigate and control charging paths very accurately.
b. The Risks to Security and Safety -
Collisions between Aircraft in Flight are a significant safety risk as the systems must be perfectly coordinated and synchronized.
c. The charging drones are heavier than regular drones due to the need for larger batteries and as a result cost more to produce due to the larger size and weight of battery needed to maintain the same power level.
d. Weather Conditions Can Impact Accuracy -
Weather conditions such as wind and rain will affect the accuracy of the charging glide paths of charging drones.e. High Cost of Development -
The development cost of this type of technology is extremely high because it is expensive to conduct studies, tests and certification on Charging Technology.7. Development Status at Present
The technology to charge drones via other drones is still experimental, universities, government and defence organisations, and private sector drone manufacturers are working on prototype testing. Although it is likely that commercial applications will require time to develop on a large scale, many of the successful trials using this technology demonstrate a significant potential. Therefore, limited operational deployments of drone-drone charging technology may occur within the next several years within defence-related, research, or emergency service organisations.
8. The Future of Charging for Drones Using Drones:
With improved battery technology and AI, drone-to-drone charging will likely become more efficient and Secure With that in mind, we will continue to develop better systems for drone-to-drone charging.
Some possible future developments of drone-to-drone include:
a. Fully automated Coordination for Charging.
b. The Ability for an AI to control Docking.
c. Overhead Wireless (lightweight) and energy distribution.
d. Networks with multiple drones will enable us to operate drones nearly 24/7 changing how we perceive aerial Missions.
e. AI-based energy prediction will help drones decide the right time and source for charging to avoid power loss.
9. Conclusion:
Dronesthat can charge themselves whilst flying are a very important development in drone technology. By allowing drones to charge in the air rather than on the ground, many of the limitations that have hampered the use of UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles), such as battery performance, would be eliminated.
Despite obstacles, there are also advantages to this new technology and the industry is moving towards utilizing and improving upon it. As more research is conducted and as technology evolves, the method of charging will be a critical element in building smart, long, and reliable Aerial operations in the future. The very air we breathe has become not just an airspace, it also has the potential to serve as a source of energy!