Introduction:
Introduction:
Modern drones have come a long way from being simple radio-controlled toys. Today, they can hover precisely, fly autonomously, and return safely to their launch point — all thanks to one essential technology: GPS. The Global Positioning System (GPS) module inside a drone plays a crucial role in navigation, stabilization, and safety.
Whether it’s for aerial photography, agriculture, mapping, or delivery systems, GPS modules help drones perform complex tasks with incredible accuracy. In this blog, we’ll explore how GPS works in drones, the technology behind it, and why it’s one of the most important components for UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) operation.
1. What Is a GPS Module?
1. What Is a GPS Module?
A GPS module is a small electronic device inside a drone that receives signals from satellites orbiting Earth. These signals help determine the drone’s exact position, altitude, and speed in real time.
Most drones use a combination of GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems) such as:
- GPS (United States)
- GLONASS (Russia)
- Galileo (Europe)
- BeiDou (China)
By accessing multiple satellite systems, modern GPS modules improve accuracy, reliability, and coverage — even in remote or urban areas where signals may be weak.
2. How Does GPS Work in a Drone?
GPS works through triangulation, calculating the drone’s position based on signals received from at least four satellites. Each satellite transmits a signal containing the exact time and its position in space.
The GPS module inside the drone measures how long it takes for these signals to arrive. Using this information, the drone’s flight controller can calculate:
- Latitude and longitude (position on Earth)
- Altitude (height above sea level)
- Velocity and direction (movement over time)
This continuous data exchange allows the drone to maintain stability, follow pre-set paths, and respond accurately to pilot commands.
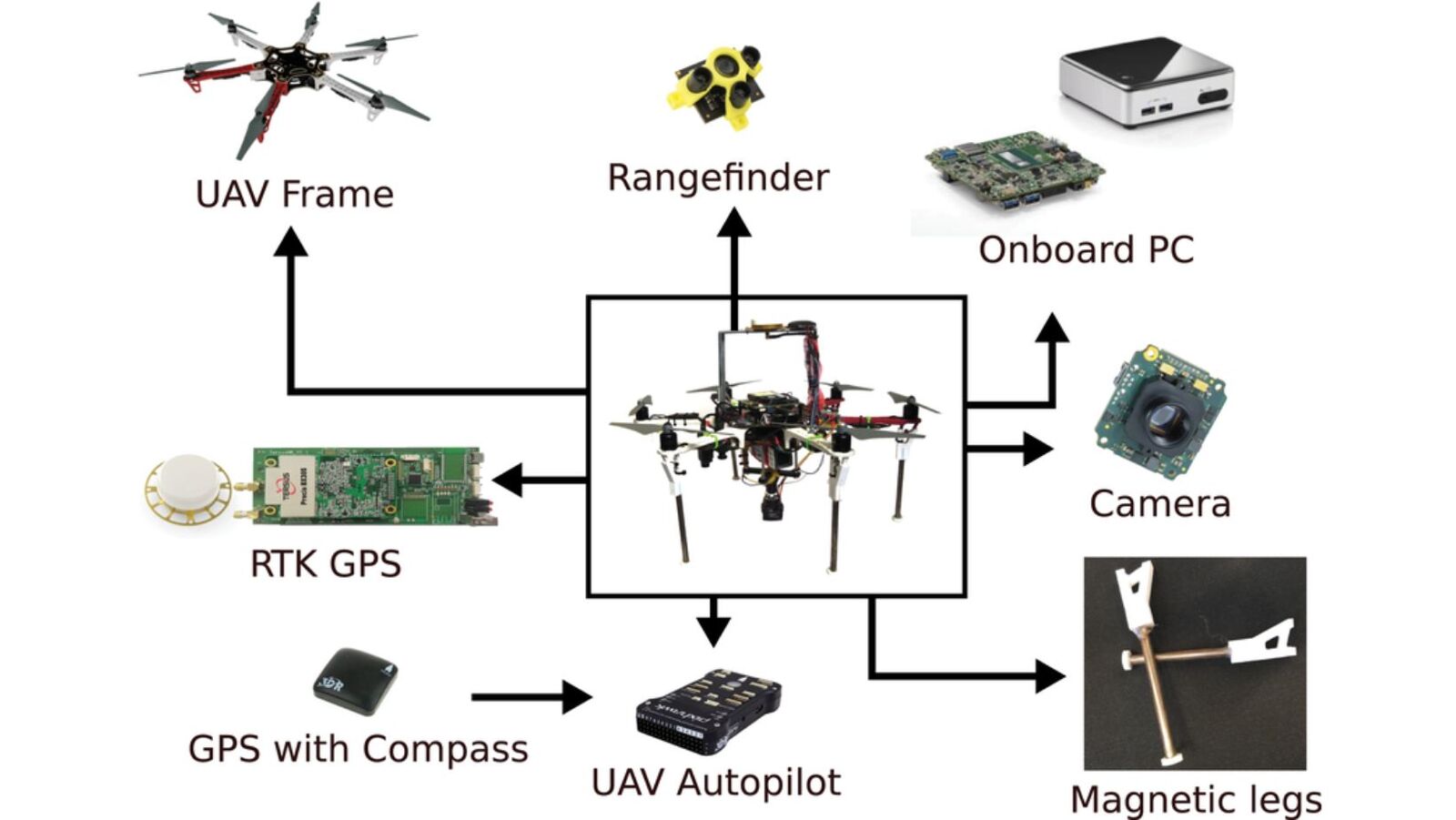
3. Components of a GPS Module
3. Components of a GPS Module
A GPS module typically includes:
- Antenna – Receives satellite signals.
- Receiver chip – Processes incoming signals.
- Processor – Calculates position, speed, and time data.
- Communication interface – Sends information to the flight controller (usually via UART, I²C, or CAN bus).
Some advanced modules also include compass sensors (magnetometers) for heading direction and barometers for improved altitude accuracy.
Let’s look at some of the most important functions enabled by GPS modules in drones:
I. Position Hold / Loiter Mode
When you stop controlling the drone, GPS helps it hold its position automatically. It hovers steadily over one spot, adjusting for wind or drift.
II. Return-to-Home (RTH)
If your drone loses signal or battery power, GPS allows it to automatically return to its takeoff point. This feature prevents loss or crash incidents and improves safety.
III. Waypoint Navigation
GPS enables autonomous flight paths. You can pre-program specific waypoints on a map, and the drone will fly along that route without manual control.
IV. Geofencing
To ensure safety, GPS helps create virtual boundaries. The drone will not fly outside designated zones, preventing it from entering restricted airspace.
V. Speed and Distance Measurement
GPS allows the drone to calculate how fast and how far it has traveled. This data is important for mapping, delivery, and flight analytics.
VI. Follow-Me Mode
In this mode, the drone locks onto your GPS position (from a controller or mobile device) and follows you automatically — perfect for filming outdoor activities.
VII. Stabilized Flight and Altitude Control
GPS data helps drones maintain balance and altitude even in windy or uneven conditions. This makes it easier for pilots to capture smooth, stable footage.5. Types of GPS Modules for Drones:
5. Types of GPS Modules for Drones:
There are different kinds of GPS modules available depending on the drone’s purpose:
- RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) GPS Modules
- Deliver centimeter-level precision using real-time corrections from a base station.
- Common in industrial, mapping, and surveying drones.
- PPK (Post-Processing Kinematic) Modules
- Record GPS data during flight for later correction.
- Ideal for mapping tasks that don’t require real-time accuracy.
- Hybrid GPS Modules (GPS + Compass + Barometer)
- Combine multiple sensors for better stability and heading control.
- Common in professional aerial photography drones.
6. Why GPS Matters in Drones:
6. Why GPS Matters in Drones:
GPS technology is more than just navigation — it’s the backbone of safe and efficient drone operation. Here’s why it matters:
· Improved Accuracy
GPS ensures precise control, positioning, and flight stability — crucial for professional applications like surveying and inspection.
· Autonomous Operations
Without GPS, drones cannot perform automated missions like mapping, spraying, or delivery routes.
· Safety
Return-to-Home and geofencing functions prevent crashes and loss, providing peace of mind to pilots.
· Data Collection
GPS provides accurate coordinates for mapping and research, making drones powerful tools for data analytics.
· Efficiency
It reduces manual workload by enabling automatic takeoff, landing, and path planning.
7. Challenges and Limitations of GPS
7. Challenges and Limitations of GPS
While GPS is powerful, it’s not perfect. Some limitations include:
- Signal Interference: Tall buildings, dense trees, or magnetic interference can reduce accuracy.
- Latency: Slight delays in signal processing can affect real-time control.
- Dependence on Satellites: If satellite visibility is poor, performance may drop.
- Power Consumption: High-precision GPS modules use more power, slightly reducing flight time.
To overcome these, many modern drones use dual-band GPS, multi-GNSS, or even AI-based flight stabilization to maintain accuracy in difficult conditions.
8. Future of GPS in Drones:
8. Future of GPS in Drones:
The next generation of GPS modules is evolving rapidly. We can expect:
- Multi-frequency GNSS systems for better accuracy.
- Integration with AI for predictive navigation and obstacle avoidance.
- Fusion with vision sensors for GPS-denied environments (like indoors or tunnels).
- Miniaturization and power efficiency, allowing smaller drones to enjoy high-precision GPS.
In the near future, GPS will continue to merge with technologies like 5G and cloud-based positioning, enabling smarter, safer, and more autonomous drone operations.
9. Tips for Drone Pilots:
9. Tips for Drone Pilots:
If you’re using a GPS-enabled drone, here are a few tips:
- Always wait for a full GPS lock before takeoff.
- Avoid flying near power lines or metal structures.
- Regularly calibrate the compass.
- Check satellite signal strength before long flights.
- Use RTK modules for professional projects that require high precision.
Conclusion:
GPS modules have transformed drones from remote-controlled gadgets into intelligent aerial systems. They make flight safer, navigation easier, and data more accurate. Whether you’re a beginner pilot or a professional engineer, understanding how GPS works will help you make smarter decisions, plan better missions, and fly more confidently.